Your How does ocean acidification affect marine life images are available in this site. How does ocean acidification affect marine life are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the How does ocean acidification affect marine life files here. Get all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for how does ocean acidification affect marine life images information linked to the how does ocean acidification affect marine life keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our website frequently provides you with hints for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
How Does Ocean Acidification Affect Marine Life. This makes it more difficult for marine organisms such as coral and some plankton to form their shells and skeletons and existing shells may begin to dissolve. Ocean acidification isnt a new concept. Oceana acidification may cause many negative effects on a variety of marine species and ecosystems which would have rippling consequences throughout the entire ocean. The impacts of ocean acidification are uneven.
 Marine Life Can Resist Ocean Acidification By Modifying Shell Building Process At The Nanoscale Advances In From advanceseng.com
Marine Life Can Resist Ocean Acidification By Modifying Shell Building Process At The Nanoscale Advances In From advanceseng.com
Now all we have to do is stop the amount of emissions going into the air and be more mindful of what were doing. Ocean acidification is best known for its osteoporosis-like effects on shellfish which makes building and maintaining shells difficult for these creatures. Its also important to remember that the stress ocean acidification will place on marine life will not be acting in isolation. Ocean acidification affects marine life Coastal and marine ecosystems are under tremendous stress from climate change. Studies have shown that decreased pH levels also affect the ability of larval clownfish. Decreased carbonate carbonateCO 3 2- availability and increased acidity.
As well as a drop in pH marine life will have to cope with increasing temperatures changes in currents and ocean circulation patterns and in some areas existing problems of pollution or over exploitation.
Decreased carbonate carbonateCO 3 2- availability and increased acidity. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2 to live just like plants on land. Carbon has been heating up our oceans for quite some time and the effects on marine life and people are very serious and damaging to our ecosystem. Ocean acidification is expected to impact ocean species to varying degrees. Ocean acidification is best known for its osteoporosis-like effects on shellfish which makes building and maintaining shells difficult for these creatures. Southern Alaska faces the greater risk due to its dependence on susceptible species for nutrition and income the forecasted rapid change in chemical.
 Source: sailorsforthesea.org
Source: sailorsforthesea.org
Just as carbonated soda water is more acidic than flat tap water higher levels of carbon dioxide CO2 in the ocean cause the water to become more. Laboratory studies suggest changing ocean chemistry will 1 harm life forms that rely on carbonate-based shells and skeletons 2 harm organisms sensitive to acidity and 3 harm organisms higher up the food chain that feed on these sensitive. Ocean acidification is expected to impact ocean species to varying degrees. Acidification also affects other species vital to the marine ecosystem including reef-building corals and pteropods tiny snails eaten by numerous species such as fish and whales. Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive.

Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive. Calcifying species may find it difficult to produce their skeleton because ocean acidification decreases calcium carbonate saturation and. As well as a drop in pH marine life will have to cope with increasing temperatures changes in currents and ocean circulation patterns and in some areas existing problems of pollution or over exploitation. Ocean acidification paired up with other climate impacts like warming waters deoxygenation melting ice and coastal erosion pose real threats to the survival of many marine species. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2 to live just like plants on land.
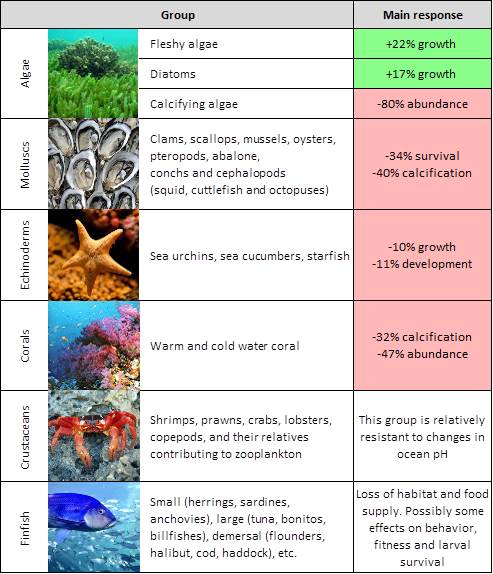 Source: coastadapt.com.au
Source: coastadapt.com.au
Acidification also affects other species vital to the marine ecosystem including reef-building corals and pteropods tiny snails eaten by numerous species such as fish and whales. One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs Marine animals interact in complex food webs that may be disrupted by ocean acidification due to losses in key. Its also important to remember that the stress ocean acidification will place on marine life will not be acting in isolation. Acidification also affects other species vital to the marine ecosystem including reef-building corals and pteropods tiny snails eaten by numerous species such as fish and whales. Decreased carbonate carbonateCO 3 2- availability and increased acidity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Its also important to remember that the stress ocean acidification will place on marine life will not be acting in isolation. Just as carbonated soda water is more acidic than flat tap water higher levels of carbon dioxide CO2 in the ocean cause the water to become more. The more acidic the ocean the faster the shells dissolve. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2 to live just like plants on land. As the oceans simultaneously warm acidify and increase in PCO2 prospects for marine biota are of concern.
 Source: dolphinaris.com
Source: dolphinaris.com
Just as carbonated soda water is more acidic than flat tap water higher levels of carbon dioxide CO2 in the ocean cause the water to become more. Many of the marine organisms likely to be most affected by ocean acidification such as mollusks are important to both highly productive commercial fisheries and to traditional subsistence ways of life. Now all we have to do is stop the amount of emissions going into the air and be more mindful of what were doing. The more acidic the ocean the faster the shells dissolve. The ability of some fish like clownfish to detect predators is decreased in more acidic waters.

Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2 to live just like plants on land. Decreased carbonate carbonateCO 3 2- availability and increased acidity. Laboratory studies suggest changing ocean chemistry will 1 harm life forms that rely on carbonate-based shells and skeletons 2 harm organisms sensitive to acidity and 3 harm organisms higher up the food chain that feed on these sensitive. Its also important to remember that the stress ocean acidification will place on marine life will not be acting in isolation.
 Source: advanceseng.com
Source: advanceseng.com
The ability of some fish like clownfish to detect predators is decreased in more acidic waters. What are the effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms and ecosystems. Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive. Ocean acidification can negatively affect marine life causing organisms shells and skeletons made from calcium carbonate to dissolve. Calcifying species may find it difficult to produce their skeleton because ocean acidification decreases calcium carbonate saturation and.
 Source: futureoflife.org
Source: futureoflife.org
Carbon has been heating up our oceans for quite some time and the effects on marine life and people are very serious and damaging to our ecosystem. As the oceans simultaneously warm acidify and increase in PCO2 prospects for marine biota are of concern. Ocean acidification is expected to impact ocean species to varying degrees. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2 to live just like plants on land. Acidification also affects other species vital to the marine ecosystem including reef-building corals and pteropods tiny snails eaten by numerous species such as fish and whales.
 Source: nps.gov
Source: nps.gov
Ocean acidification can negatively affect marine life causing organisms shells and skeletons made from calcium carbonate to dissolve. Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive. Ocean acidification isnt a new concept. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2 to live just like plants on land. Acidification also affects other species vital to the marine ecosystem including reef-building corals and pteropods tiny snails eaten by numerous species such as fish and whales.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
As well as a drop in pH marine life will have to cope with increasing temperatures changes in currents and ocean circulation patterns and in some areas existing problems of pollution or over exploitation. Ocean acidification reduces the amount of carbonate a key building block in seawater. Southern Alaska faces the greater risk due to its dependence on susceptible species for nutrition and income the forecasted rapid change in chemical. One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs Marine animals interact in complex food webs that may be disrupted by ocean acidification due to losses in key. Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Oceana acidification may cause many negative effects on a variety of marine species and ecosystems which would have rippling consequences throughout the entire ocean. The more acidic the ocean the faster the shells dissolve. Southern Alaska faces the greater risk due to its dependence on susceptible species for nutrition and income the forecasted rapid change in chemical. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2. Decreased carbonate carbonateCO 3 2- availability and increased acidity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Ocean acidification impacts on fish and seaweeds Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well. Ocean acidification affects marine life Coastal and marine ecosystems are under tremendous stress from climate change. The impacts of ocean acidification are uneven. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2 to live just like plants on land. Acidification also affects other species vital to the marine ecosystem including reef-building corals and pteropods tiny snails eaten by numerous species such as fish and whales.
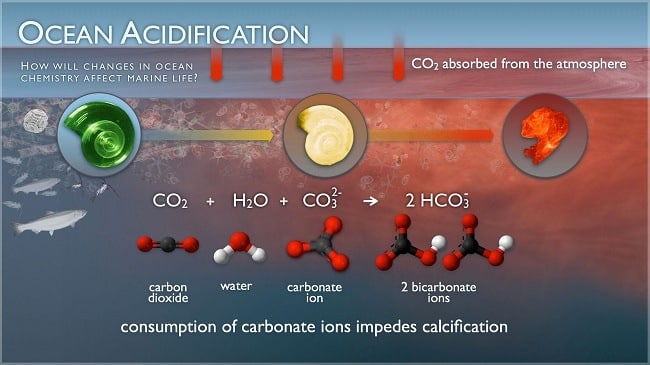 Source: marineinsight.com
Source: marineinsight.com
As the oceans simultaneously warm acidify and increase in PCO2 prospects for marine biota are of concern. Ocean acidification impacts on fish and seaweeds Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2. As the oceans simultaneously warm acidify and increase in PCO2 prospects for marine biota are of concern. As well as a drop in pH marine life will have to cope with increasing temperatures changes in currents and ocean circulation patterns and in some areas existing problems of pollution or over exploitation.
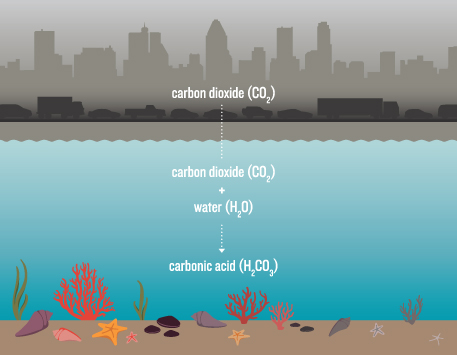 Source: ensia.com
Source: ensia.com
One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs Marine animals interact in complex food webs that may be disrupted by ocean acidification due to losses in key. How the ocean is absorbing carbon dioxide and helping global warming but its harming biodiversity coral reefs and sea life. Now all we have to do is stop the amount of emissions going into the air and be more mindful of what were doing. Ocean acidification is expected to impact ocean species to varying degrees. Acidification also affects other species vital to the marine ecosystem including reef-building corals and pteropods tiny snails eaten by numerous species such as fish and whales.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2. Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive. Ocean acidification is best known for its osteoporosis-like effects on shellfish which makes building and maintaining shells difficult for these creatures. Laboratory studies suggest changing ocean chemistry will 1 harm life forms that rely on carbonate-based shells and skeletons 2 harm organisms sensitive to acidity and 3 harm organisms higher up the food chain that feed on these sensitive. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs Marine animals interact in complex food webs that may be disrupted by ocean acidification due to losses in key. The impacts of ocean acidification are uneven. Ocean acidification can negatively affect marine life causing organisms shells and skeletons made from calcium carbonate to dissolve. Studies have shown that decreased pH levels also affect the ability of larval clownfish. Ocean acidification impacts on fish and seaweeds Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs Marine animals interact in complex food webs that may be disrupted by ocean acidification due to losses in key. Laboratory studies suggest changing ocean chemistry will 1 harm life forms that rely on carbonate-based shells and skeletons 2 harm organisms sensitive to acidity and 3 harm organisms higher up the food chain that feed on these sensitive. Now all we have to do is stop the amount of emissions going into the air and be more mindful of what were doing. Carbon has been heating up our oceans for quite some time and the effects on marine life and people are very serious and damaging to our ecosystem. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2.

Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2. Photosynthetic algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean as they require CO 2. Calcifying species may find it difficult to produce their skeleton because ocean acidification decreases calcium carbonate saturation and. Ocean acidification reduces the amount of carbonate a key building block in seawater. Southern Alaska faces the greater risk due to its dependence on susceptible species for nutrition and income the forecasted rapid change in chemical.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title how does ocean acidification affect marine life by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





